A study finds an increased risk of developing a productive SARS-CoV-2 infection in obese people. Obesity is known to predict worse outcomes and higher mortality for those with COVID-19. Masanori Aikawa and colleagues sought to determine if obesity also affected the likelihood of getting ill in the first place.
Study finds higher SARS-CoV-2 risk in obese individuals retrieved 27 August 2024 from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-08-higher-sars-cov-obese-individuals.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Medicine Research Health Research News Health Research Health Science Medicine Science
Nigeria Latest News, Nigeria Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Study finds rates of obesity-related cancer are rising sharply in young Chinese peopleObesity-related cancer rates in China were rising at an alarming 3.6% every year between 2007 and 2021 while non-obesity-related cancers remained stable, according to the first comprehensive study published August 22 in the journal Med.
Study finds rates of obesity-related cancer are rising sharply in young Chinese peopleObesity-related cancer rates in China were rising at an alarming 3.6% every year between 2007 and 2021 while non-obesity-related cancers remained stable, according to the first comprehensive study published August 22 in the journal Med.
Read more »
 SARS-CoV-2 detected in common wildlife speciesSARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, is widespread among wildlife species, according to Virginia Tech research published Monday (July 29, 2024) in Nature Communications.
SARS-CoV-2 detected in common wildlife speciesSARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, is widespread among wildlife species, according to Virginia Tech research published Monday (July 29, 2024) in Nature Communications.
Read more »
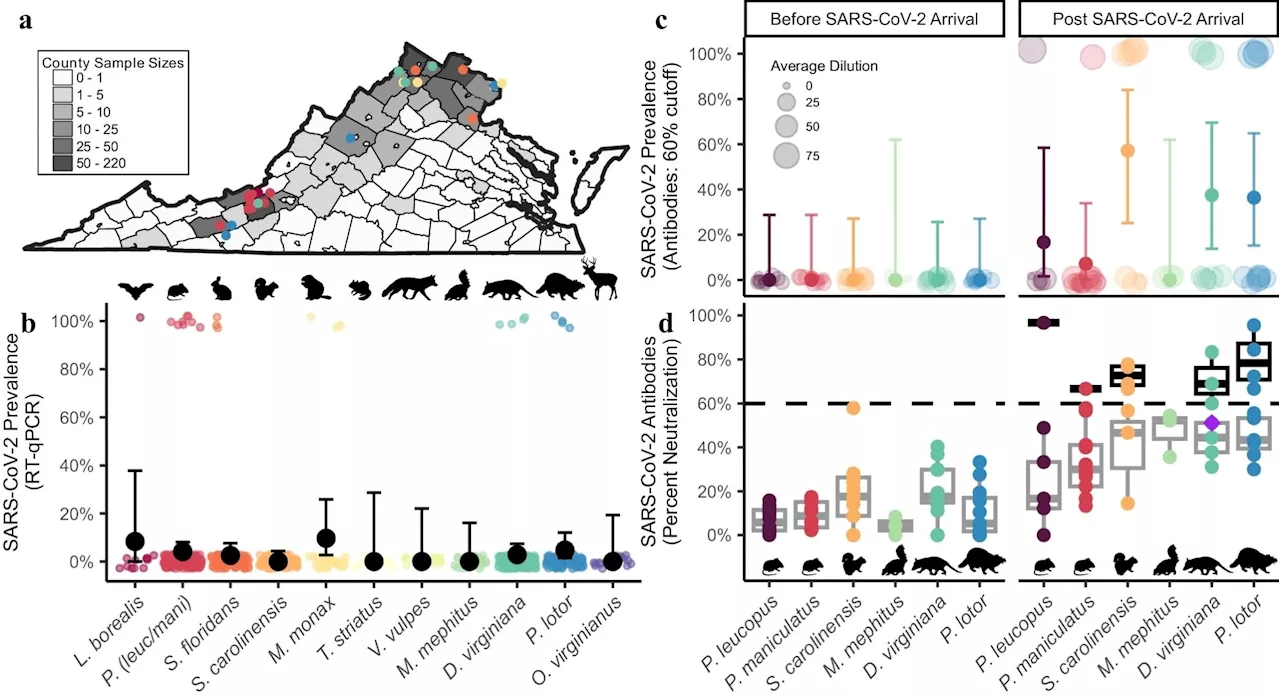 Wildlife species show high SARS-CoV-2 exposure linked to human activityResearchers found SARS-CoV-2 RNA in six wildlife species and higher seroprevalence in high human activity areas. Seven new human-to-animal transmission events of the Omicron variant were identified.
Wildlife species show high SARS-CoV-2 exposure linked to human activityResearchers found SARS-CoV-2 RNA in six wildlife species and higher seroprevalence in high human activity areas. Seven new human-to-animal transmission events of the Omicron variant were identified.
Read more »
 Mucosal COVID-19 vaccine prevents airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2The impact of mucosal versus intramuscular vaccine immunization on airborne infection and transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in Syrian hamsters.
Mucosal COVID-19 vaccine prevents airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2The impact of mucosal versus intramuscular vaccine immunization on airborne infection and transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in Syrian hamsters.
Read more »
 SARS-CoV-2 protein linked to onset of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in childrenSt. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists have identified a link between a SARS-CoV-2 protein and the onset of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
SARS-CoV-2 protein linked to onset of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in childrenSt. Jude Children's Research Hospital scientists have identified a link between a SARS-CoV-2 protein and the onset of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
Read more »
 Cross-reactive T cells link SARS-CoV-2 to autoimmune triggers in MIS-CResearch identifies cross-reactive T cells targeting both SARS-CoV-2 and human SNX8 protein, providing insights into the autoimmune mechanisms driving MIS-C in children.
Cross-reactive T cells link SARS-CoV-2 to autoimmune triggers in MIS-CResearch identifies cross-reactive T cells targeting both SARS-CoV-2 and human SNX8 protein, providing insights into the autoimmune mechanisms driving MIS-C in children.
Read more »
