Predicting mRNA degradation to improve vaccine stability TAMUEngineering
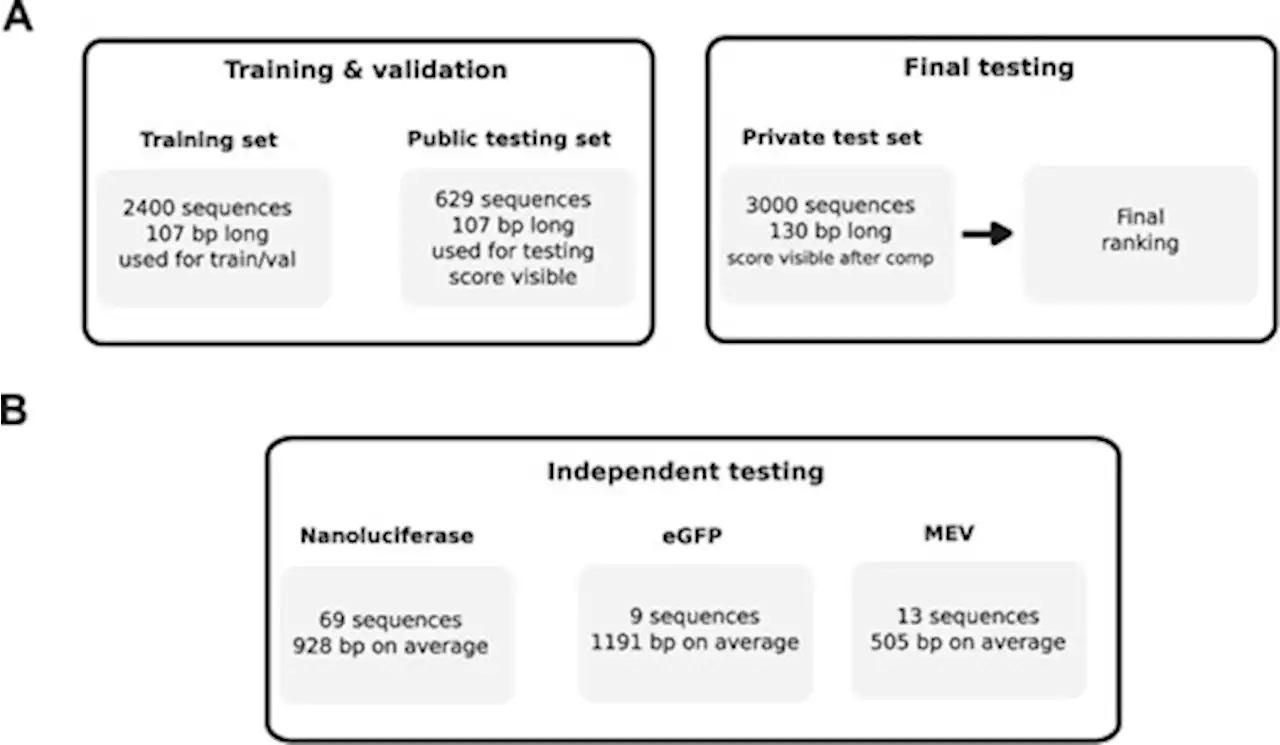
], and it is our hope the RNAdegformer will aid design of more stable mRNA vaccines that can withstand harsher conditions than current ones. It is important to note, however, that there is still significant gap between errors on the 107 bp mRNA OpenVaccine public set sequences and the 130 bp mRNA OpenVaccine private set sequences, both due to difference in sequence length and diversity. Actual COVID-19 candidates are even longer and modeling those remains a challenge in the future.
In summary, we have developed a convolution and transformer-based deep learning platform toward prediction of mRNA degradation and half-lives. Our work has demonstrated success in RNA stability and half-life predictions. We believe that by further development and optimization, we will solve many challenges including understanding RNA degradation and structure relationships, aiding next-generation mRNA therapy development, and more.
Using unsupervised , supervised and semi-supervised learning in conjunction with each other, we demonstrate that RNAdegformer outperforms the top solution in OpenVaccine at predicting RNA degradation rates at each position of a given RNA sequence, a task of great importance to predict and produce stable mRNA vaccines and therapeutics.
RNAdegformer generalizes better to predict half-lives of sequences much longer than those in the training dataset compared with other machine learning and dynamic programming algorithms. RNAdegformer also reveals feature importance in predicting mRNA degradation through the usage of leave-one-feature-out test, advancing our understanding of RNA degradationS.H. and B.G conceived the project. R.S.provided critical feedback on the analysis of RNA sequences and biological context. S.H. implemented the deep learning algorithms and participated in the OpenVaccine challenge. Q.S. supervised the project and provided guidance. S.H., B.G. and R.S.
Nigeria Latest News, Nigeria Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Molecular characterization of oriental eyeworm (Thelazia callipaeda) detected from raccoon (Procyon lotor) and Japanese raccoon dog (Nyctereutes viverrinus) in Kanto region, Japan - Parasites & VectorsBackground The oriental eyeworm Thelazia callipaeda (Spirurida: Thelaziidae) is an emerging parasitic ocular nematode of carnivores and humans. In domestic animals and humans, the infection causes varying degrees of inflammation and lacrimation, and wild carnivores represent an important reservoir. In this study we examined the infection status and molecular characterization of T. callipaeda in two urban carnivores, raccoons Procyon lotor and wild Japanese raccoon dogs Nyctereutes viverrinus, in the Kanto region of Japan. Methods From January 2020 to December 2021, 193 carcasses including 178 raccoons and 15 raccoon dogs were examined for the presence of worms in the eye. The worms from infected animals (one worm per host) were morphologically identified as T. callipaeda. Worms (1–5 worms per host) were subjected to genetic analysis using mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene sequences. Results The prevalence of T. callipaeda in raccoons and Japanese raccoon dogs was 20.2% (36/178) and 13.3% (2/15), respectively. The cox1 sequences from 56 worms from 38 animals revealed three haplotypes (h9, h10, and h12). Analysis of multiple worms for five raccoons showed co-infection of two different haplotypes (h9 and h10) in a single host. Comparing our data with published sequences, three sequences obtained from raccoons and raccoon dogs shared the same haplotypes as those reported in humans, dogs, and cats in Japan. Conclusions Our findings show a high prevalence of T. callipaeda in raccoons, suggesting that this invasive carnivore species serves as an important natural reservoir of T. callipaeda in the Kanto region of Japan, an area with the highest human population of the country. Graphical Abstract
Molecular characterization of oriental eyeworm (Thelazia callipaeda) detected from raccoon (Procyon lotor) and Japanese raccoon dog (Nyctereutes viverrinus) in Kanto region, Japan - Parasites & VectorsBackground The oriental eyeworm Thelazia callipaeda (Spirurida: Thelaziidae) is an emerging parasitic ocular nematode of carnivores and humans. In domestic animals and humans, the infection causes varying degrees of inflammation and lacrimation, and wild carnivores represent an important reservoir. In this study we examined the infection status and molecular characterization of T. callipaeda in two urban carnivores, raccoons Procyon lotor and wild Japanese raccoon dogs Nyctereutes viverrinus, in the Kanto region of Japan. Methods From January 2020 to December 2021, 193 carcasses including 178 raccoons and 15 raccoon dogs were examined for the presence of worms in the eye. The worms from infected animals (one worm per host) were morphologically identified as T. callipaeda. Worms (1–5 worms per host) were subjected to genetic analysis using mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene sequences. Results The prevalence of T. callipaeda in raccoons and Japanese raccoon dogs was 20.2% (36/178) and 13.3% (2/15), respectively. The cox1 sequences from 56 worms from 38 animals revealed three haplotypes (h9, h10, and h12). Analysis of multiple worms for five raccoons showed co-infection of two different haplotypes (h9 and h10) in a single host. Comparing our data with published sequences, three sequences obtained from raccoons and raccoon dogs shared the same haplotypes as those reported in humans, dogs, and cats in Japan. Conclusions Our findings show a high prevalence of T. callipaeda in raccoons, suggesting that this invasive carnivore species serves as an important natural reservoir of T. callipaeda in the Kanto region of Japan, an area with the highest human population of the country. Graphical Abstract
Read more »
 6-Axis Photonics Alignment System based on Air BearingsFrom Physik Instrumente (PI) GmbH & Co KG Apr 6 2023 Auburn, MA – PI USA, a premium supplier of precision motion systems and air bearings for alignment, precision motion, metrology and automation...
6-Axis Photonics Alignment System based on Air BearingsFrom Physik Instrumente (PI) GmbH & Co KG Apr 6 2023 Auburn, MA – PI USA, a premium supplier of precision motion systems and air bearings for alignment, precision motion, metrology and automation...
Read more »
 Devon-based surf forecaster Magic Seaweed loses name in mergerThe global forecaster's founder says the loss is 'emotional', but he is 'excited for the future'.
Devon-based surf forecaster Magic Seaweed loses name in mergerThe global forecaster's founder says the loss is 'emotional', but he is 'excited for the future'.
Read more »
![]() Data-leak flaw in Qualcomm, HiSilicon-based Wi-Fi AP chipsWPA stands for will-provide-access, if you can successfully exploit a target's setup
Data-leak flaw in Qualcomm, HiSilicon-based Wi-Fi AP chipsWPA stands for will-provide-access, if you can successfully exploit a target's setup
Read more »
 Alistair McGowan to take on Mastermind to help Shropshire-based hedgehog charityImpressionist Alistair McGowan, who lives in the Ludlow area, will be going on Mastermind to raise money for the British Hedgehog Preservation Society.
Alistair McGowan to take on Mastermind to help Shropshire-based hedgehog charityImpressionist Alistair McGowan, who lives in the Ludlow area, will be going on Mastermind to raise money for the British Hedgehog Preservation Society.
Read more »