Individuals with compromised immunity and persistent COVID-19 infections can harbor drug-resistant variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which have the potential to spread to the general population found researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine, the College of Veterinary Medicine at Cornell University and the National Institutes of Health's (NIH)...
Weill Cornell Medicine Sep 18 2024 Individuals with compromised immunity and persistent COVID-19 infections can harbor drug-resistant variants of the SARS -CoV-2 virus, which have the potential to spread to the general population found researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine , the College of Veterinary Medicine at Cornell University and the National Institutes of Health's National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases .
The risk in emerging mutations is the possibility of transmitting these new resistant variants to the general population with fewer viable treatment options available. We have to come up with better treatments for immunocompromised patients and consider investigating combinations of therapies." Unique challenges in treating persistent COVID infections While people with working immune systems can typically clear SARS-CoV-2 within days, those who are immunocompromised may continue to harbor and shed the virus for longer, even without symptoms. They also often receive multiple antiviral treatments over time, which may lead to the emergence of drug-resistant variants.
Combination therapies may be the answer The researchers found that when they grew the isolated virus in lab cell cultures, two drugs simultaneously were effective in clearing the drug-resistant strain. "These findings indicate that combination therapy may be a better option to treat COVID-19 in highly vulnerable immunocompromised patients," said co-senior author Dr.
SARS-Cov-2 Allergy Antibody Antiviral Drug Cell Covid-19 Drugs Immunity Infectious Diseases Medicine Monoclonal Antibody Protein Remdesivir Research Sotrovimab Veterinary Virus
Nigeria Latest News, Nigeria Headlines
Similar News:You can also read news stories similar to this one that we have collected from other news sources.
 Synergistic mutations found in omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2Certain changes in the genetic material of pathogens can alter their ability to infect human cells or protect them better from defense by the immune system. Researchers were able to observe this effect particularly impressively in the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Synergistic mutations found in omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2Certain changes in the genetic material of pathogens can alter their ability to infect human cells or protect them better from defense by the immune system. Researchers were able to observe this effect particularly impressively in the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Read more »
 Antiviral-resistant variants of SARS-CoV-2 can emerge in immunocompromised peopleIndividuals with compromised immunity and persistent COVID-19 infections can harbor drug-resistant variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which have the potential to spread to the general population found researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine, the College of Veterinary Medicine at Cornell University and the National Institutes of Health's (NIH)...
Antiviral-resistant variants of SARS-CoV-2 can emerge in immunocompromised peopleIndividuals with compromised immunity and persistent COVID-19 infections can harbor drug-resistant variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which have the potential to spread to the general population found researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine, the College of Veterinary Medicine at Cornell University and the National Institutes of Health's (NIH)...
Read more »
 Study reveals how SARS-CoV-2 triggers diabetes by destroying pancreatic cellsResearchers from Weill Cornell Medicine have used a cutting-edge model system to uncover the mechanism by which SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, induces new cases of diabetes, and worsens complications in people who already have it.
Study reveals how SARS-CoV-2 triggers diabetes by destroying pancreatic cellsResearchers from Weill Cornell Medicine have used a cutting-edge model system to uncover the mechanism by which SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, induces new cases of diabetes, and worsens complications in people who already have it.
Read more »
 Newly discovered antibody can neutralize all known variants of SARS-CoV-2Researchers have discovered an antibody able to neutralize all known variants of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, as well as distantly related SARS-like coronaviruses that infect other animals.
Newly discovered antibody can neutralize all known variants of SARS-CoV-2Researchers have discovered an antibody able to neutralize all known variants of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, as well as distantly related SARS-like coronaviruses that infect other animals.
Read more »
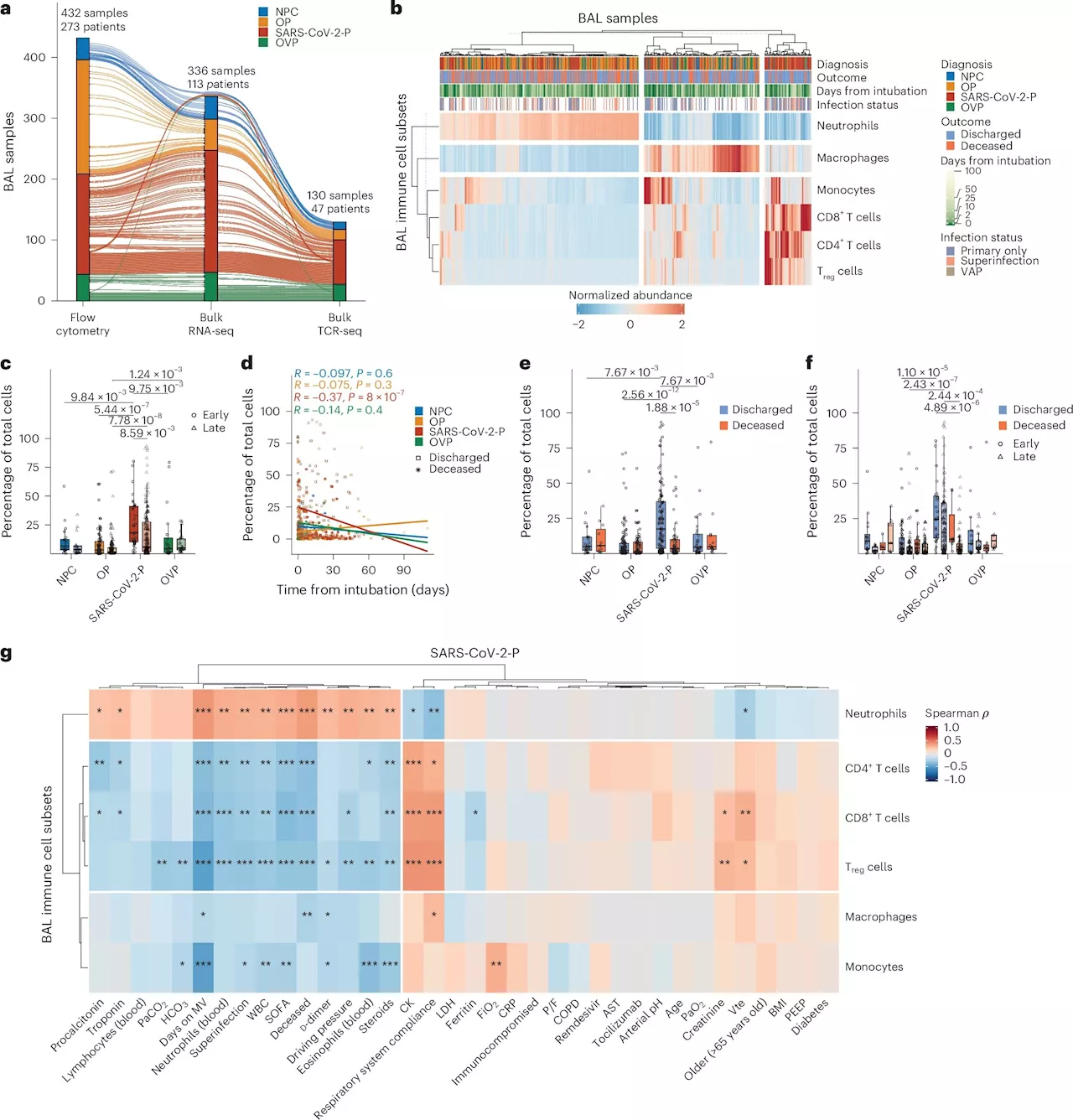 T-cell responses influence patient outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, study findsNorthwestern Medicine investigators have identified distinct T-cell responses associated with patient outcomes in unvaccinated individuals with severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, according to findings published in Nature Immunology.
T-cell responses influence patient outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, study findsNorthwestern Medicine investigators have identified distinct T-cell responses associated with patient outcomes in unvaccinated individuals with severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, according to findings published in Nature Immunology.
Read more »
 Novel monoclonal antibody appears effective at neutralizing numerous SARS-CoV-2 variantsA monoclonal antibody appears effective at neutralizing the numerous variants of SARS-CoV-2, as well as related viruses in animals that could pose a threat if they were to begin spreading in people.
Novel monoclonal antibody appears effective at neutralizing numerous SARS-CoV-2 variantsA monoclonal antibody appears effective at neutralizing the numerous variants of SARS-CoV-2, as well as related viruses in animals that could pose a threat if they were to begin spreading in people.
Read more »